Let’s talk about the normal knee xray, knee joint anatomy, and knee replacement surgery. It appears to be on the minds of many folks in the Greatest Generation at this time in their lives.
That, in turn, means radiographers will be performing an increasing number of knee xrays of all kinds: sunrise, tunnel, weight-bearing, etc.
Normal Knee Xray Anatomy
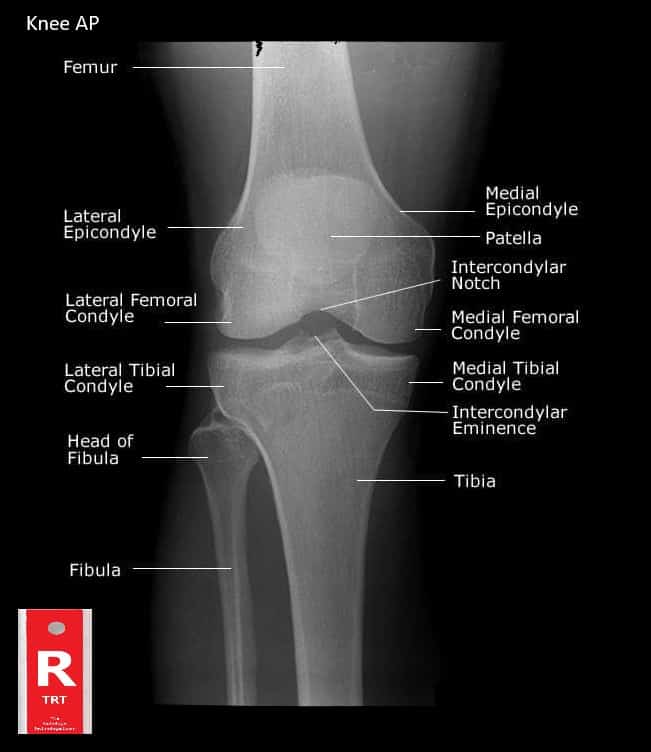
The knee is a hinge joint shapes by the joining of the thigh bone (Femur) and two bones of the lower leg (Tibia). The Fibula (see picture) is in the area of the knee but does not directly articulate with the joint.
The Patella, or knee cap, is another bone in the area of the knee joint.
The knee is the biggest hinge joint in the body and carries the most concern since it bolsters the whole weight of the body above it.
Therefore, the terminal ends, or condyles, of the femur and tibia that meet at the knee are fairly large structures.
The bones of the knee articulate forward and in reverse like a big shock absorber for the body.
The kneecap, or patella, keeps the tibia from moving too far forward when the leg is twisted.
The articulating (meeting) surfaces of the femur and tibia condyles are exceptionally smooth and are isolated by a slight hole. This “hole” is called the Intercondylar Notch.
The femur and the tibia are held together at the joint by an arrangement of tendons that connect the bones together.
Normal knee xray anatomy
The bones are padded by a synovial film and by layers of ligaments on the outside of every condyle.
The whole knee joint, including the kneecap, is encompassed in a capsular mechanical assembly that enables the kneecap to swing all over openly on the front surface of the femur.
The quadriceps muscle of the thigh causes knee augmentation (fixing of the leg), while various other upper leg muscles cause the correlative movement, flexion, or bowing, of the leg.
Some turn of the lower leg is likewise conceivable when the knee bow; however, the fixing of solid parallel tendons at the joint averts revolution when the leg is straight.
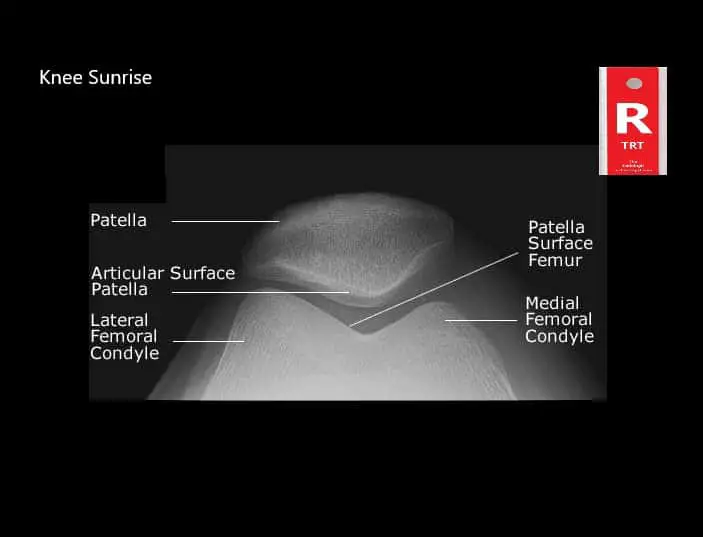
Albeit well-adjusted for the descending transmission of the body’s weight, the structure of the knee itself offers little protection from the horizontal dislocation of the femur and tibia condyles during movement.
So the knee’s solidness relies upon the quality of the encompassing tendons and muscles.
Most normal knee wounds, including bone dislocations and torn ligaments, mirror the defenselessness of the knee joint to the parallel removal of its bones.
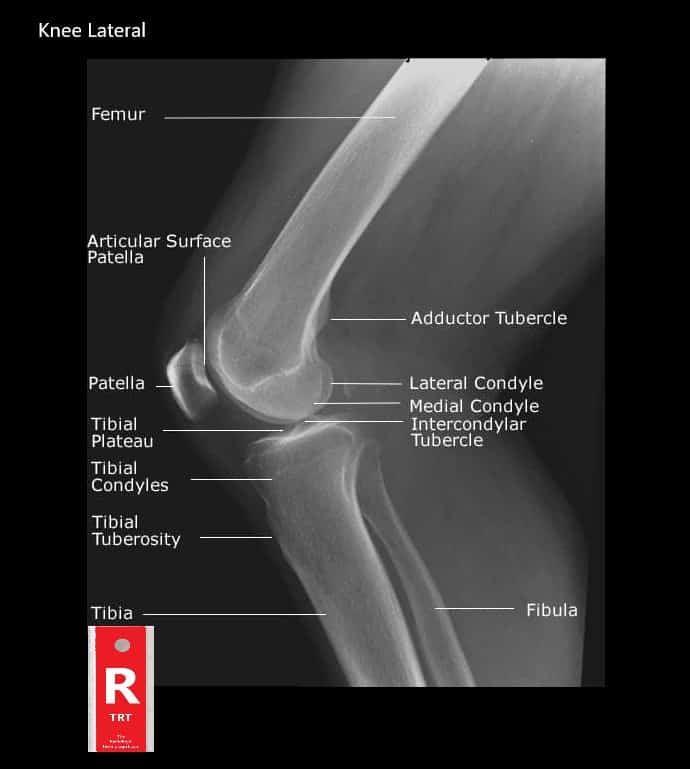
Normal Knee Xray
How to Cope and Deal with Osteoarthritis.
Arthritis is not just one single disease as we may have understood earlier. It is an illness that can be related to joint pain and joint disease.
We have a full article here on Osteoarthritis – Living with Degenerative Joint Disease.
Though this is a widespread concern, yet we fail to understand it completely. This disease which attacks us in more than a hundred different types, do not bias and targets all age groups, genders, and communities.
However, women and older adults are more prone to this virus.
A common symptom of this disease is the swelling and stiffness in the knee.
It is painful and can limit us from doing our normal regular physical activities. Symptoms can be erratic and may result in mild and severe pain.
Arthritic knee pain causes difficulty while bending and stretching the knee.
Osteoarthritis is one of the most significant causes of disability in adults in the United States (Zhang, 2010).
Types of Arthritis:
Let us discuss some 5 types of Arthritis in brief.
Osteoarthritis (OA):
It is the most common type of Arthritis that eats away the joint cartilage; a firm and flexible connective tissue, in a slow process.
You will experience discomfort in your physical movement like climbing upstairs, which will also be visibly red around the knee.
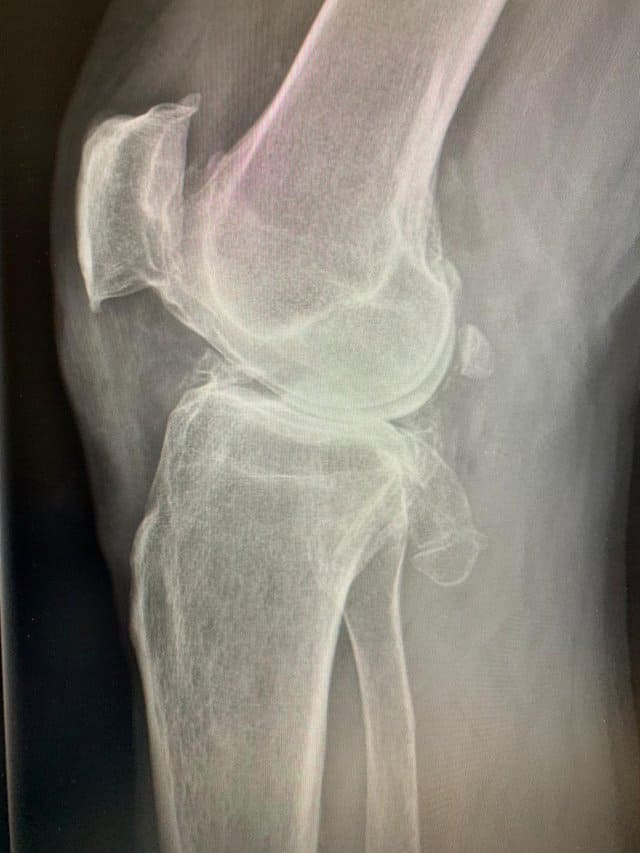
The pain is also likely to occur from other parts of the joint such as synovium, bone, and ligaments.
This illness is most likely to occur after middle age.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA):
This affects the joints and other body organs; the attack comes from the body’s immune system.
The bacteria in RA becomes excited and destroys healthy tissues in the body.
Further, you may quickly become tired, experience a loss of appetite, fever and red-blood-cell count may also decrease.
In other words, you may be anemic. The immune system attacks the synovium and leaves permanent damage causing deformity if overlooked.
The pain can also occur in the bones and ligaments. Most people suffering from this disease have antibodies known as rheumatoid factors (RF) in their blood.
Psoriatic Arthritis:
This auto-immune inflammatory Arthritis affects people who have psoriasis.
Psoriasis is a skin disorder causing redness, scaly rash on your elbows, ankles, knees, feet and other parts of the body.
The disease can either be mild or severe, and the symptoms are usually swollen joints, stiffness, and pain.
Damage can worsen if left untreated.
Thumb Arthritis:
This disability occurs when the cartilage wears away at the base of the thumb joints.
It causes severe pain and swelling, making it challenging to turn doorknobs, opening jars, etc.
This type of problem requires splints and medication and surgery for severe Arthritis.
Septic Arthritis:
This includes a painful infection in a joint caused by germs traveling from other parts of the body through the bloodstream.
It can affect the hips, shoulders and other joints besides the knee. Children and older adults are more vulnerable to it.
Antibiotics and needle draining of the connective bones are usually a remedy for septic arthritis.
How Accurate is a Knee X-Ray?
X rays can help a doctor see the inside of the joints. There are several types of imaging modalities that can help to see arthritis:
X-ray (Radiography):
It is a simple test where an X-ray beam passes through the knee, creating a two-dimensional image of the bones forming the joints.
This process gives details of specific dense structures like bone, bone spurs, and large effusions. They are highlighted and appear white on film.
However, diagnosing soft tissue like muscle, tendons, ligaments and the meniscus are vague and appear grey, providing very little detail.
An X-ray can be prescribed if the patient has been experiencing knee pain for several weeks.
Xrays have less ionizing radiation for the patient and are typically the first stop on the trial to analyze the knee.
Computerized Axial Tomography (CAT):
This scan produces multiple images of the knee where every single image can be combined and create a three-dimensional picture.
The scan detects soft tissues better than other conventional Xrays.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI):
The process involves a strong magnetic link to the computer to provide a clear image of both the soft tissues and bones.
The scanning machine produces black and white images and shades of grey of the knee joints.
With the clear details of the tissues visible, this procedure is especially useful to identify injuries to the tendons, ligaments, cartilage, menisci and the swelling area.
Diagnosis using normal knee xray:
On your visit to the doctor, he will examine your symptoms related to arthritic knee pain like swollen joints and physical motion decrease.
You will also be required to do a blood test and x-ray, which can also help in distinguishing the type of Arthritis you may have.
Let us quickly look into how many ways we can diagnose osteoarthritis.
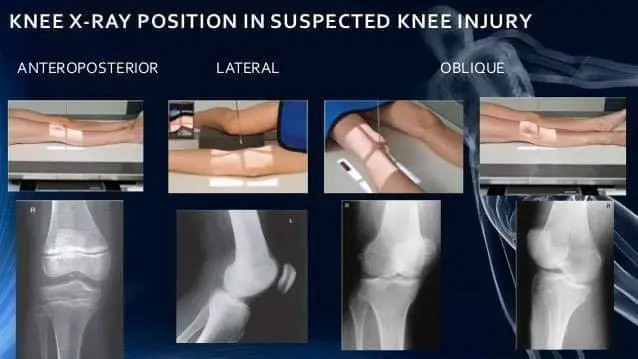
Knee (AP Weight Bearing View):
Most physicians and clinicians agree that a standing knee x-ray is essential for arthritis patients rather than the non-weight bearing position.
It is a standard projection to study the knee joint, proximal tibia, fibula, distal femur, and the patella.
This standing position is used to get the images of the knees with its natural anatomical position. It also shows the effect of a person’s weight on the knee joint.
Steps:
- The suspected arthritis patient is made to stand against the upright detector with the ankle joint and the knee touching the sensor.
- The leg should stretch.
- The knee should not rotate.
Knee (Rosenberg View)
For the knee, a more specialized procedure is required to detect early signs of Osteoarthritis (OA) for suspected patients.
It is the initial study for anyone having symptoms of the disease.
It is more sensitive than the regular weight-bearing view to detect knee joint space narrowing.
Steps:
- The patient should stand against the upright detector with the knees bent in about 45 degrees. This position provides discomfort to the patient, providing better results for the doctor studying the problem.
Tunnel View Knee X-Ray (Knee PA Axial Camp)
In this procedure, the patient should lie in a supine position: lying with face upwards.
Moreover, The knee stretches from 40-45 degrees with knee support for rest.
It demonstrates the posterior aspect of the femoral condyles, the intercondylar eminence of the tibia and the intercondylar notch.
What type of treatment treats Arthritis?
There can be several ways to manage inflammatory pain in the joints; however, there is no permanent cure for it. Check out some of the answers to help you get that relief from this health predator.
Exercise:
First, you should visit the doctor for advice before you start any exercise regime.
The absence of physical activity can lead to muscle loss, and additional weight gain as this disease can severely reduce the joint motions.
Further, with medication, Arthritis can significantly affect one’s daily life. Most technologists recommend Physical training to decrease pain and stiffness and avoid further damage gradually.
With exercise as a treatment plan, it will help you:
- Maintain normal joint movement
- Increase muscle strength and flexibility
- Keep Cartilage tissue and bone strong and healthy
- Reduce the weight pressure of the joints
- Improve cardiovascular fitness.
Arthritis Knee Brace:
Braces are suitable for people with arthritic knee pain. This equipment can help your knee stability while walking and enhance your mobility as it takes off the pressure on the joints.
Moreover, You can stand and move around with more confidence while this brace unloads the stress generating from the knee joints caused by osteoarthritis.
People using knee braces review that a lot of comfort and relief has to the strain they suffer from this disease.
Knee Replacement Surgery:
It is also a knee arthroplasty involving a medical process to remove the knee joint weight-bearing base.
This is done mainly to relieve a patient from pain and physical deformity.
The surgery is one of the most common bone surgeries. The decision must make between you and your doctors.
Knee replacement surgery is an option when most of the other treatments you have tried doesn’t seem to give a positive result.
It involves cutting away the arthritic bone and replaced with a prosthetic joint.
Different types of knee surgery:
Knee replacement surgery:
It is a conventional surgery where the base of the thigh and shin bone connecting to the knee is replaced.
Kneecap replacement:
This procedure involves the replacement of the under-surface of the kneecap
Partial knee replacement surgery:
This surgery is done through a smaller cutting, unlike the total knee replacement. People with Arthritis affecting only one side of the knee usually opt for this process.
Complex knee replacement surgery:
A patient who has undergone several knee replacement surgeries or having severe Arthritis may advise to undergo this operation.
Tips for better knee health
Do’s:
- Choose activities that build the muscles around the joints
- Add low-aerobic routines like cycling and walking etc.
- Use Pain relief medication and cream for temporary comfort.
- Therapy, acupuncture, and massage, etc. can also be an ideal physical and emotional integration.
- Understanding the condition of the type of Arthritis you have and if any of the damage joints.
- Involve your doctor, family, and friends to manage the pain.
- Inform your doctor of any changes in the pain.
- Use good posture, regular body motions, balance activities (don’t overdo).
- Manage weight, quit smoking as it stresses the connective tissues.
Dont’s:
- Inflammatory foods like fried and processed, sugars, dairy products, alcohol, tobacco, salt, and preservatives.
- Activities involving high impact like running and jumping etc.
- Overdo pain relief medication.
- Negative thoughts
Conclusion:
People having Arthritis should maintain a healthy lifestyle, visit the doctor regularly and continue taking the prescribed medication.
This worldwide disability can affect our daily activities and limit our movements if left untreated or attended.
Hence, Take precautions against the disease worsening.
References:
Zhang, Y., & Jordan, J. M. (2010). Epidemiology of osteoarthritis. Clinics in geriatric medicine, 26(3), 355–369. doi:10.1016/j.cger.2010.03.001

