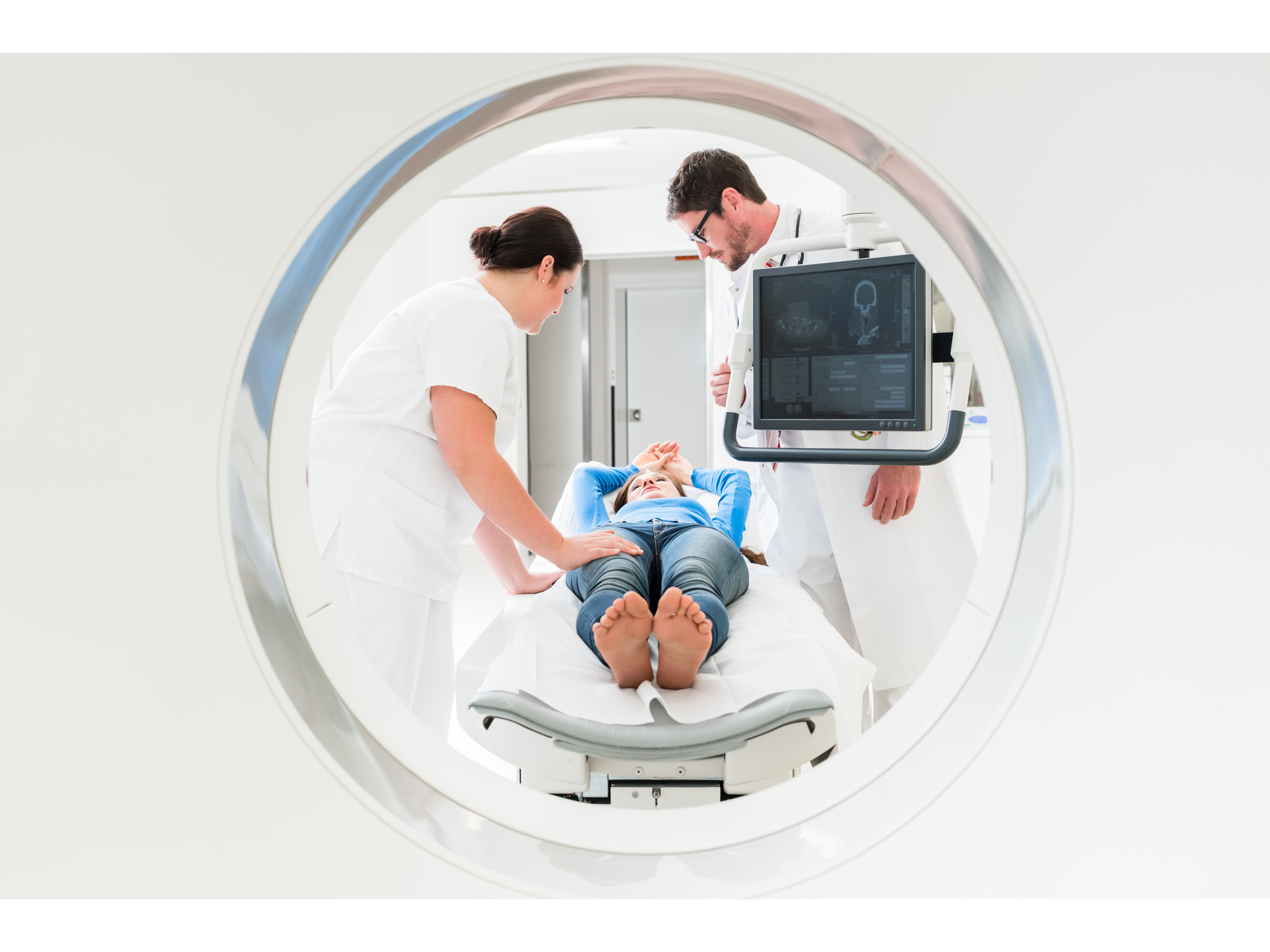
The landscape of medical diagnostics and treatment is constantly evolving, with advanced technologies offering new insights and capabilities. Among these advancements, Image-Guided Biopsy, Radiomics, and Dual-Energy Computed Tomography (CT) stand out as game-changers.
In this blog, we delve into each of these areas, exploring how they are reshaping patient care and treatment strategies.
Image-Guided Biopsy: Enhancing Accuracy and Safety
Background and Purpose: Image-guided biopsy has emerged as a critical tool in the diagnostic arsenal of modern medicine. This technique enhances the precision of tissue sampling, thereby improving diagnostic accuracy while minimizing patient discomfort and procedure-related risks.
Methods: By integrating imaging techniques such as ultrasound, CT, or MRI, clinicians can accurately target tissue for biopsy. This approach is especially beneficial in accessing tumors or lesions that are difficult to reach, ensuring that the biopsy is both safe and representative of the disease.
Results: The outcomes of image-guided biopsies have been overwhelmingly positive. Patients experience fewer complications, and the samples obtained are of higher quality, leading to more accurate diagnoses and better-informed treatment plans.
Conclusion: The future of image-guided biopsy looks promising. As imaging technologies continue to advance, we can expect even greater precision and safety in biopsy procedures, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes.
Radiomics: Revolutionizing Prediction of Treatment Responses
Introduction: Radiomics, the extraction of quantitative features from medical images, is transforming the way clinicians predict treatment responses. This technique allows for a more nuanced understanding of tumor characteristics.
Radiomics Models Development: These models are developed by analyzing medical images using algorithms to identify patterns not visible to the human eye. This process involves extracting a large number of features from the images, followed by rigorous analysis to identify those most relevant to treatment outcomes.
Clinical Characteristics: By integrating patient data, radiomics models can offer personalized predictions. This holistic approach provides a more accurate assessment of how different treatments might work for individual patients.
Model Performance and Comparison: Comparative studies have shown that radiomics models can be highly effective in predicting treatment responses, outperforming traditional methods in many cases.
Discussion and Conclusion: The potential of radiomics in personalized medicine is enormous. With ongoing advancements, these models could become a standard part of treatment planning, offering tailored therapies based on detailed image analysis.
Dual-Energy CT: Expanding Diagnostic Capabilities
Background and Purpose: Dual-Energy CT is a breakthrough in diagnostic imaging. By using two different energy levels, it provides more detailed information about tissue composition than standard CT.
Methods: This technique involves capturing images at multiple energy levels, then analyzing these images to differentiate between various types of tissues and substances. This process is particularly effective in identifying and characterizing tumors and other pathological conditions.
Results: The use of Dual-Energy CT in clinical practice has led to more accurate diagnoses and better-informed treatment decisions. Its ability to distinguish between different types of tissues enhances the precision of diagnostic imaging.
Conclusion: The role of Dual-Energy CT is set to expand further in medical imaging. Its potential in improving diagnostic accuracy is immense, making it a valuable tool in the early detection and treatment of diseases.
Clinical Implications: The impact of Dual-Energy CT in clinical practice is significant. It offers clinicians a more nuanced view of diseases, leading to more effective treatment strategies.
Limitations and Future Directions: While promising, the technology does have limitations, such as the need for further validation in larger patient cohorts. Future research is expected to focus on enhancing the technology’s capabilities and reducing limitations.
In summary, Image-Guided Biopsy, Radiomics, and Dual-Energy CT are at the forefront of medical innovation. They are not only enhancing diagnostic accuracy and safety but also paving the way for personalized treatment approaches. As these technologies continue to evolve, they promise to bring about significant improvements in patient care and treatment efficacy.